
This is important to avoid spreading the infection.

How Is Gonorrhea Diagnosed?įor diagnosis, the health care provider asks about symptoms and sexual activity and examines the sexual organs, including the pelvic area for women. Other symptoms may include sore throat, low-grade fever tender lower abdomen (belly) pain in knees, ankles, or elbows and a rash on the palms of the hands. Symptoms in women include pain or burning when urinating, yellow or green vaginal discharge that can be bloody, bleeding between periods, and pain during sex. They include creamy green-yellow discharge from the penis, pain when urinating, and painful and swollen testicles.

These include: Pain or burning feeling when you pee Abnormal discharge from the vagina that may be yellowish or bloody Bleeding between periods People with penises are more likely to have symptoms if they get gonorrhea. Symptoms in men usually start within 2 weeks after exposure. If they do, gonorrhea symptoms show up within about a week of being infected. They often don’t know that they have gonorrhea until they have other problems. Most men have symptoms when first infected, but many women may have very mild or no symptoms. It spreads very easily by having sex with an infected person.

The cause is a type of bacteria named Neisseria gonorrhoeae. More than half a million people in the United States get gonorrhea every year. Epididymitis is inflammation or infection of the epididymis, a long tube above and behind each testicle. Urethritis is inflammation (swelling, redness) of the urethra, the tube that carries urine and semen through the penis. In men, it can cause infections called urethritis and epididymitis.
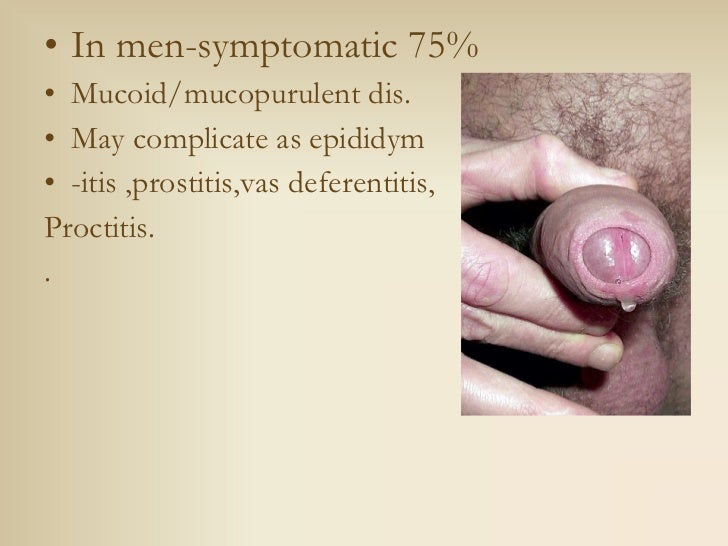
In women, it can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and can be passed from pregnant women to their babies during birth. Untreated gonorrhea can lead to serious problems, including pharyngitis, tonsillitis, severe arthritis, and bloodstream infection. It usually affects the sex organs but may also occur in other parts of the body, such as the eyes, throat, and joints. Indications for hospitalization for PID include the presence of a tubo-ovarian abscess, severe illness with systemic symptoms, pregnancy, human immunodeficiency virus infection, and failure to respond to outpatient oral treatment (within 48–72 hours) or inability to tolerate the oral treatment.Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that is caused by bacteria. Providers should have a low threshold for diagnosing and treating PID because untreated PID can have serious long-term complications for young women. Nucleic acid amplification tests are the most sensitive and specific for the detection of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis, and they can be performed on provider- or patient-collected swabs. Most infected persons, however, are asymptomatic. Abnormal vaginal bleeding during or after sex or between periods. Anal itching, discomfort, bleeding, or discharge. Symptoms may include: Painful or frequent urination.
#Gonorrhea symptoms women discharge series
( 1)( 2) This review, the second in a 2-part series on STIs, focuses on infections that may cause abnormal vaginal or penile discharge, including trichomonas, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). In women, the early symptoms are sometimes so mild that they are mistaken for a bladder infection or vaginal infection. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) disproportionately affect young people, with more than half of the infections occurring in youth aged 15 to 25 years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
